I have just found a very interesting news, for many people, all over the world: “Some Spanish scientists design a drug capable of curbing a wide range of autoimmune diseases such as asthma or psoriasis”.

Spanish scientists have designed a drug capable of curbing a variety of autoimmune diseases such as asthma, psoriasis, Crohn's disease or multiple sclerosis, but without blocking the body's natural response, against infections caused by pathogens.
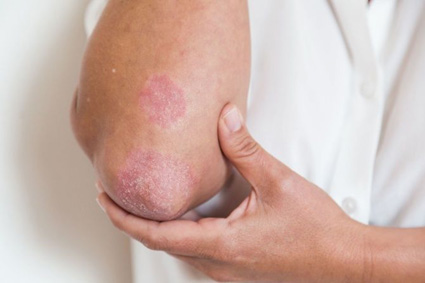
Psoriasis on one arm
The compound, an inhibitor of T lymphocyte activation, is the result of the work of 32 Spanish researchers from the CSIC, the Institute of Biomedical Studies August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS), the National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC) and the Princess Hospital of Madrid, mainly.
The study, led by Balbino Alarcón of the Center for Molecular Biology Severo Ochoa, has been published in Science Translational Medicine.
"The new drug, which has been tested in healthy volunteers and has passed the toxicity tests, on the contrary of many of the current treatments of autoimmune diseases, that are based on the use of antibodies and are administered intravenously, is taken orally and has, in addition, a long-lasting effect", Alarcón has explained, in declarations to Efe.
In mouse models "we have seen that it has effects even when the compound ceases to be administered, which means that a treatment, for a short time, could be enough to cause the symptoms of the disease to go away, without having to medicate the patient for life", Alarcón has noted.
The compound is not immunosuppressive but allows, at least in mice, the body to activate the natural response, against pathogens (viruses, bacteria, parasites or fungi), while being effective in autoimmune diseases.
In this way, it ends with the usual problem of the current drugs, that, to treat autoimmune diseases, cancel the body's natural ability to fight infections, "which makes these patients very sensitive to infections".
Alarcón has detailed that the compound inhibits the activation of T lymphocytes, which are responsible for detecting the body's antigens, which can be either own (in tissues and organs) or foreign (those that pose a threat and a potential infection).
For their work, T lymphocytes have an essential receptor: the receptor for TCR antigens, which transmits information to the interior of the lymphocyte cell, to indicate that it has detected or recognised an antigen (external or not), information that is transmited through different proteins, that are inside the cell. One of them is the NCK. "When TCR recruits NCK or joins it inside the cell, it transmits information indicating that it has recognised an antigen".
The drug inhibits or blocks the interaction among TCR and NCK and thus "makes T cells stop responding to their own antigens, in an autoimmune disease, and to fight the external antigens of an infectious process. It is its differential effect”.
The company Artax Biopharma (USA, UK, Spain) has carried out Phase I trials of the drug, with healthy volunteers, and it is now studying the possibility of taking it to clinical stage, in different diseases.
Well, I hope this discovery works well, in different hospitals, and can cure many patients.
Until my next post, kind regards,
Luis.
Sponsored by Costaluz Lawyers.
Please click below:
