"Next stop, Banco de España." When you travel on line 2 of the Madrid metro and approach this station, little would you know that just a few meters away you can find one of the best-kept treasures in Spain, the Bank of Spain's gold deposit chamber? A chamber that contains a third of Spain’s total reserve of this precious metal.

The central headquarters of the Bank of Spain is one of the most representative buildings of Madrid and of the Spanish architecture of the 19th and early 20th centuries. For the construction of the current headquarters of the Bank of Spain, the palace of the Marquis of Alcañices was acquired in 1882, located on Calle de Alcalá around the Paseo del Prado. The first stone was laid on July 4, 1884, in a ceremony attended by King Alfonso XII and the monumental building was inaugurated in 1891.
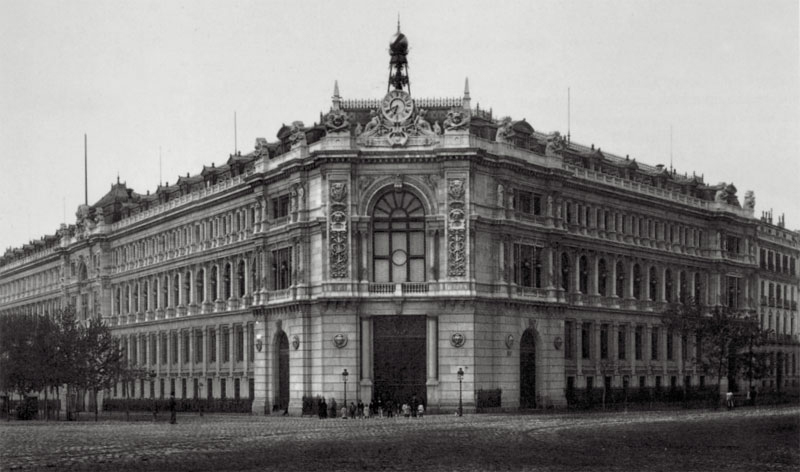

Construction of the vault for the safekeeping of the gold began in late 1932 and was completed in two and a half years, with 260 workers working three shifts. Its approximate cost was nine and a half million pesetas. The inauguration took place shortly before the Civil War, during which it served as a refuge from the bombings for the families who inhabited the bank building.
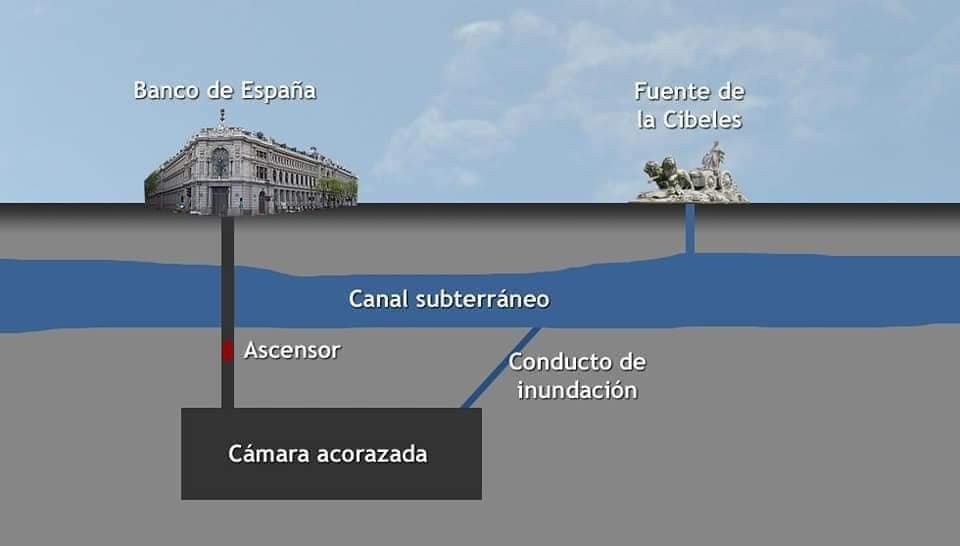
The chamber is 35 meters deep and its surface is 2,500 square meters. Its design seems to be inspired by a similar construction of the vault of the Vienna Savings Bank.

The construction is made of reinforced concrete and molten cement, and to carry it out it was necessary to pipe and divert the waters present in the subsoil, some 25 meters deep, as it pressed on the walls of the chamber. This water corresponds to the Las Pascualas stream, which runs almost at surface level along the Castellana and which was, in its day, channelled underground, running down Calle Alcalá and feeds into the fountain of Cibeles.
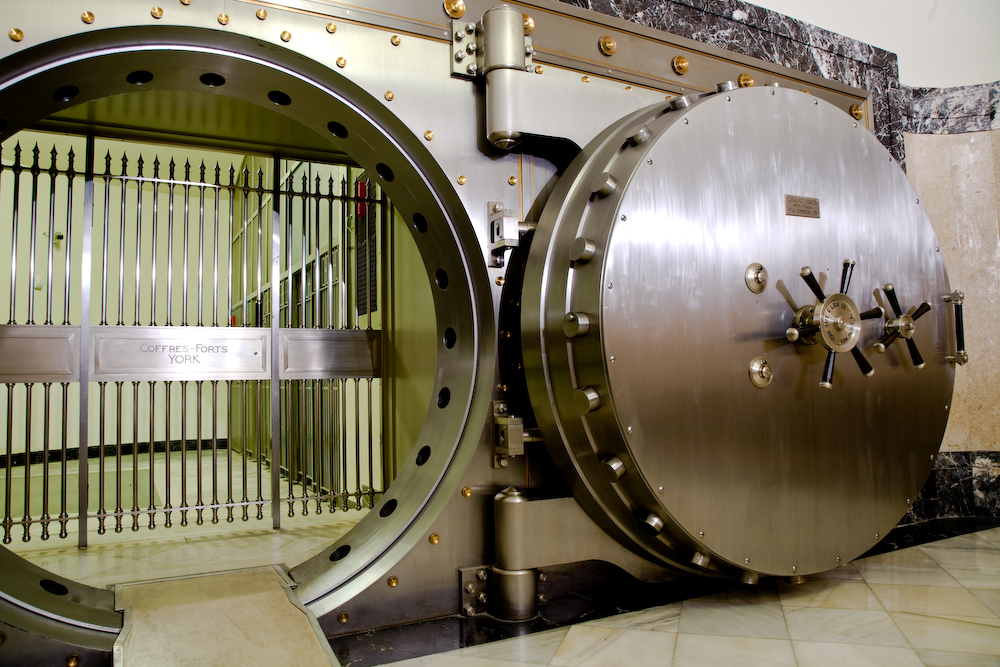
Access to the chamber is through several armoured doors, the first of which weighs around 16 tons and was manufactured in Pennsylvania, USA, by Cofres Forts York (York Safe & Lock Company). The other smaller doors, but also armoured, were manufactured by the same company. Its weight ranges between 15 and 8 tons. To carry out the descent of these doors down into their position, steel cables were used that could only be used once, due to the wear they suffered when supporting the immense weight of the doors.
The armoured door has a very small tolerance, of tenths of a millimetre, so that even the slightest impurity in the arch prevents it from fitting correctly and the anchor points from being activated. In addition, the door is made of steel, but not stainless, so care must be taken to maintain it, and it should always be covered with a thin layer of petroleum jelly to prevent it from rusting.
The gold chamber houses the numismatic collection of the Bank of Spain, only comparable to the collections of the Archaeological Museum or the Royal Mint, and part of the gold reserves. Inside it, a third of the Spanish gold reserve is stacked on shelves made by the engineer Eiffel. Some even say that the chamber could contain 38 Nazi gold bars with which Switzerland paid Spain between 1941 and 1945 and that they have the III Reich shield with its swastika printed on them.
What is clear is that most of the coins that make up this collection come from popular subscriptions made during the Civil War, donations, sometimes voluntary, for the financing of the army and the deposits constituted from 1937, as a result of the Decree of Nationalization of Foreign Exchange and Gold. This Decree obliged all citizens to deliver the gold in paste or coin that they had in their power to replace the gold reserves that the republican government had sent to Moscow as payment for war supplies.
These deliveries were made in the form of deposits and most of them are not recoverable because the depositors chose to collect in cash the gold value of their coins. Others, whose coins had a higher numismatic or sentimental value, preferred to keep the deposit in the hope of recovering them when the regulations allowed. Some of the latter are still being returned, provided that the claimant can prove his right to the deposit.
The collection, of great numismatic value, is made up of more than half a million pieces and includes coins of very diverse origin since it collects not only the numismatic history of the Iberian Peninsula but there are also Greek, Roman, Byzantine pieces, from Hispanic America, French or British. It also has a complete collection of gold dollars, minted since the 17th century. There is also a less numerous collection of silver pieces.

The Bank of Spain owns 9.1 million troy ounces of gold, according to 2014 data, which are deposited in its own vaults and in three other places abroad, including the Bank for International Settlements in Basel, for reasons of logistical ease, in case it was necessary to mobilize these reserves. Another place where part of the gold is conserved is Fort Knox, in the United States. A standard gold bar weighs 400 troy ounces, just under 12 and a half kilos.

To get to the vault, you have to overcome various obstacles and as you can imagine, it is not very easy. That said, it sounds like an adventure for Indiana Jones and this location is the used in the new season of the Money Heist!
- The first obstacle is a 16-ton steel door. To open the door, three keys are necessary: those of the general manager, the controller and the cashier.
- Then you reach a fortified elevator that is the only way to descend through a vertical tunnel of 36-38 meters. Of course, you need a different key to use the elevator.
- Once down, you go through an underground corridor until you reach another 14-ton steel door.
- Once through that door, there is a moat. To cross it you have to use a retractable bridge as in the Middle Ages.
- Behind the bridge is another 8-ton armoured door. This is the access to the vault that contains the gold. In addition to this, there are sensors, cameras and all kinds of surveillance devices.
If an alarm were to go off, all doors would automatically close and the moat would be completely flooded within minutes thanks to the underwater stream channelling into the fountain of Cibeles. The police or the army would arrive in less than 5 minutes and it would all be over.
But ultimately it is Cibeles who is safeguarding Spain’s gold!
Not once has anyone ever attempted to rob the Bank of Spain.

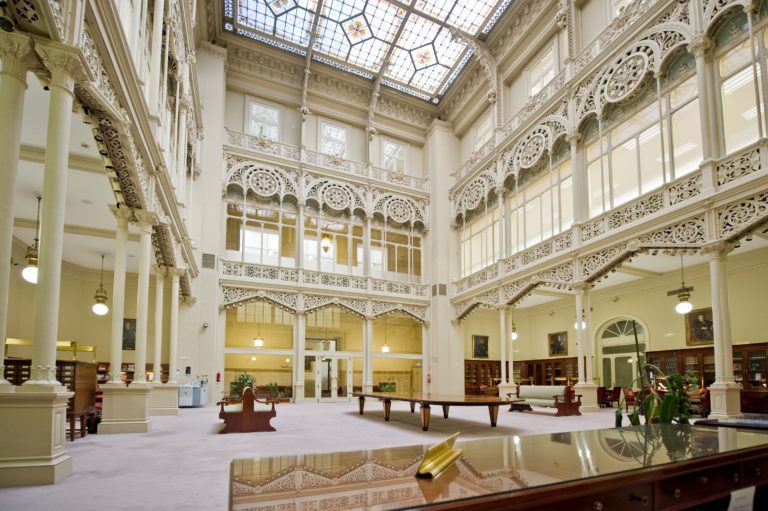
Inside the original building from 1891, the main staircase and the patio stand out, which was the general reception area and which today occupies the library, to which a cast-iron structure was added, commissioned from the Mieres Factory.
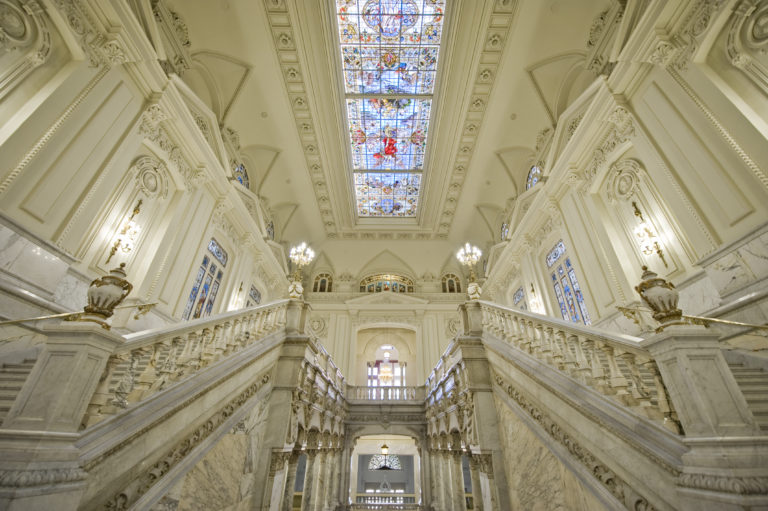


The monumental Carrara marble staircase, which is accessed from the Paseo del Prado door, is a sample of the most traditional architecture, designed by the Bank's architects and executed by Adolfo Areizaga from Bilbao. Next to it are magnificent Symbolist-style stained glass windows commissioned from the German company Mayer, with numerous allegorical figures.
With the expansion decided in 1927 and completed in 1934, the new operations yard, with a height of 27 meters and an area of about 900 square meters, departs from the classic concepts and includes some examples of Art Deco, such as the upper window or the clock, a decorative and functional piece located in the centre of the patio. Also noteworthy is the roundabout, which serves as an interior link between the two buildings.